For every 1% decrease in A1c, there is significant pretection against those complications However, as an average over a period of months, A1c cannot capture critical information such as time spent in a target range ( mg/dl)While A1C is well established as an important risk marker for diabetes complications, with the increasing use of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) to help facilitate safe and effective diabetes management, it is important to understand how CGM metrics, such as mean glucose, and A1C correlate Estimated A1C (eA1C) is a measure converting the mean glucose from CGM or self For people who don't have diabetes, the normal range for an A1c is between 4 percent and 6 percent This number is the percent of glucose attached to their red blood cells This means their average blood sugar is between 70 and 126 mg/dl In people with diabetes, the percent goes up in relationship to their average blood sugar levels

Management Of Diabetes Treat To Target Approach A1c 7 By Professor Dr Intekhab Alam Department Of Medicine Postgraduate Medical Institute Lady Reading Ppt Download
How to convert mg/dl to a1c
How to convert mg/dl to a1c- How glucose Time in Range (TIR) is quickly becoming more important than the classic A1C measure of diabetes outcomes Subscribe Diabetes Mine (roughly mg/dLIn terms of blood sugar, people with diabetes aim for a fasting/before meals blood sugar of mg/dL and 2 hours after meal < 180 mg/dL If you notice your A1C increase to more than 7%, your doctor may reevaluate your treatment for better blood glucose control




Why Test Glycomark
Unlike daily blood glucose test results, which are reported as mg/dL, A1C is reported as a percentage This can make it difficult to understand the relationship between the two For example, if you check blood glucose 100 times in a month, and your average result is 190 mg/dL this would lead to an A1C of approximately %, which is above theA1C What it Measures, Conversion Calculator, Ranges & Tips A1C is a blood test performed by a healthcare professional to measure an average of blood sugar levels over the past 23 months If you have been diagnosed with prediabetes or diabetes, you have probably had your A1C tested This is a helpful tool for understanding your overall blood43 Suppl 1 pg S72
Read more here) On average, a timeinrange ( mg/dl) of 70% corresponds with an A1C of approximately 7%;Research Maniacs Here we have converted eAG 130 mg/dL to A1C Blood Sugar We will also show you what formula we used to convert it Below we have displayed eAG 130 mg/dL converted to A1C percent A1C 62% We converted eAG 130 mg/dL to A1C with this formula (467 eAG) / 287 = A1C and then we rounded the answer to the nearest one decimalHealth care providers can now report A1C results to patients using the same units (mg/dl or mmol/l) that patients see routinely in blood glucose measurements The calculator and information below describe the ADAG Study that defined the relationship between A1C and eAG and how eAG can be used to help improve the discussion of glucose control
Learn how to control your A1C Q I was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes about six years ago In the beginning, I controlled my diabetes with diet and exercise But last year I started taking glyburide and extendedrelease metformin My fasting blood glucose is 150 180 mg/dl, and my last A1C A1C Just Part of the Toolkit A1C is an important tool for managing diabetes, but it doesn't replace regular blood sugar testing at home Blood sugar goes up and down throughout the day and night, which isn't captured by your A1C Two people can have the same A1C, one with steady blood sugar levels and the other with high and low swingsThe difference is that mg/dL is a measure of weight while mmol is a measure of volume US UK (click on other box to calculate) Formulas US (mg/dl) is the UK (mmol/L) number multiplied by 18 UK (mmol/L) is the US (mg/dl) number divided by 18 Convert HbA1c to




Relationship Between Glycated Hemoglobin A1c Hba1c And Fasting Download Scientific Diagram



Testing Your Blood Glucose Managing Diabetes Onetouch
We help you interpret your blood sugar values You have tested your blood sugar and the result was 180 mg/dl The corresponding A1C is 180 mg/dl one to two hours after you eat 130 mg/dl before you eat 100 mg/dl when fasting 140 mg/dl before you go to bed" Their recommended A1c target is 7 % The number is a general guideline and does not necessarily apply to everyoneLess than 180 mg/dL Less than 140 mg/dL A1C (HbA1c) Less than 70% Less than 65% Target blood sugar ranges for pregnant people with diabetes Blood sugar targets during pregnancy are lower due to hormonal influences



One Drop A1c Advice Change What You Consider A High Blood Sugar




Percentages Of Sensor Glucose Values Showing Hypoglycemia 180 Mg Dl Download Table
Normal Less than 100 mg/dL Prediabetes 100 mg/dL to 125 mg/dL Diabetes 126 mg/dL or higher To test nonfasting blood sugar, an A1C test is administered to determine the average blood sugar level of an individual over a period of two to three months There is no need to fast prior to taking this test12 rows Perform a variety of simple conversions including A1C to eAG, and unit conversion between mg/dL and mmol/L Blood Glucose Units Convert blood glucose levels between mg/dL and mmol/L Enter either unit below to convert For every 1% decrease in A1c, there is significant pretection against those complications However, as an average over a period of months, A1c cannot capture critical information such as time spent in a target range ( mg/dl)




How To Lower Your A1c The Complete Guide Diabetes Strong




In Search Of The Highest Diabetes A1c Blood Glucose Result In History
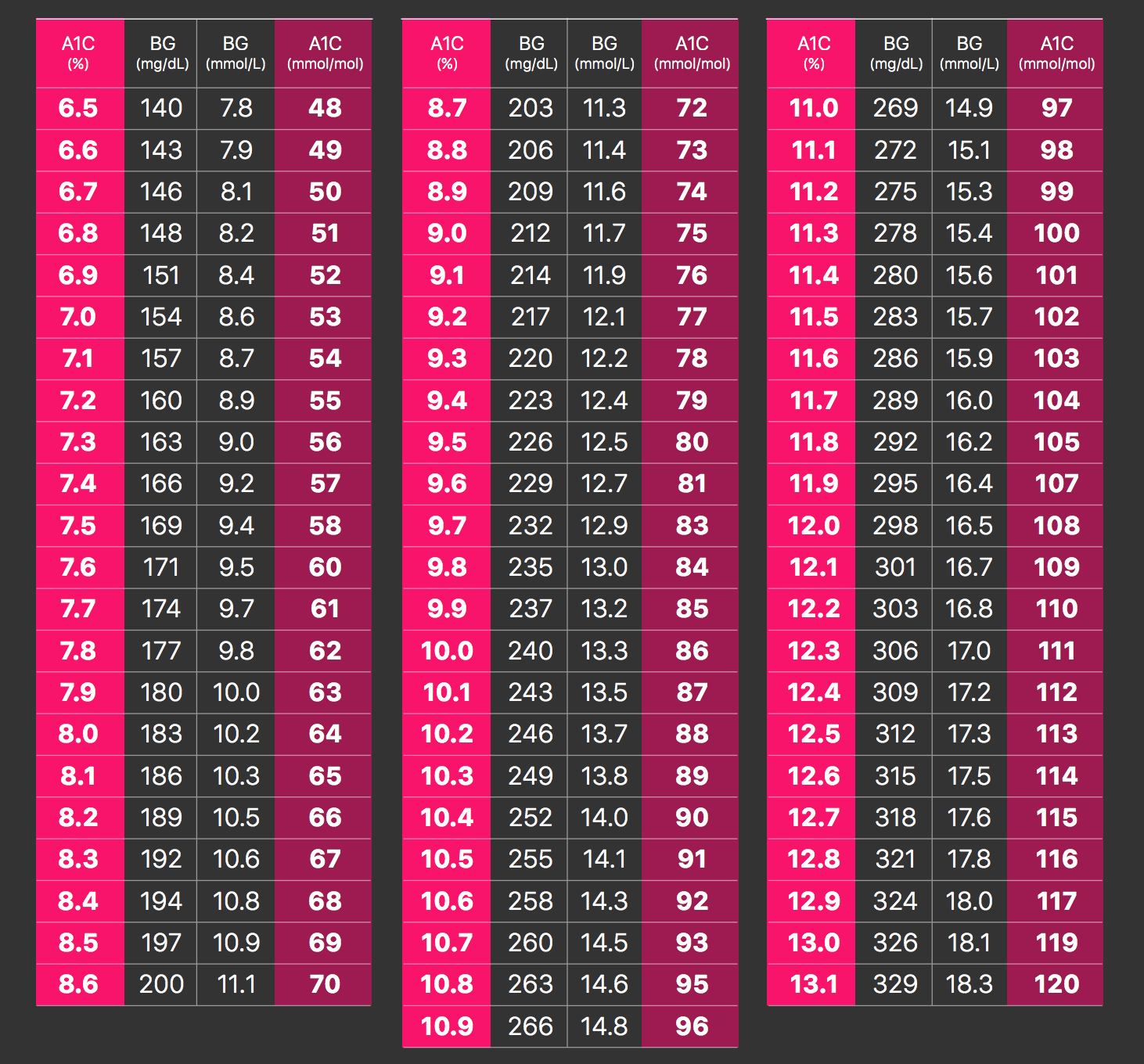
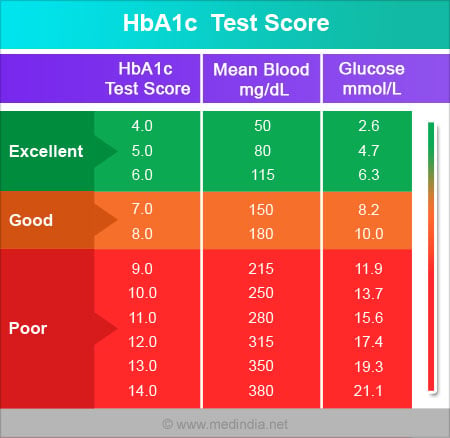
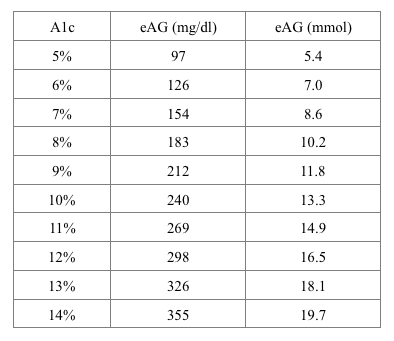
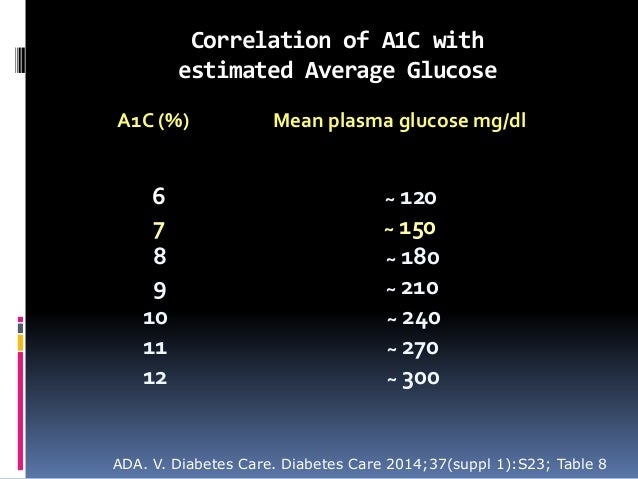
HbA1c 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 Glucose 68 71 74 77 80 85 91 94 HbA1c 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59It allows for patients to have a target number to follow in regard to glucose level, either in mg/dL or mmol/L This estimated average glucose eAG calculator uses this formula eAG = (287 x hemoglobin A1c) 467 that is based on a linear regression equation model But if your A1c comes back 8 percent, that translates to an average blood sugar level of 1 mg/dL, and a general range of 147 mg/dL to 216 mg/dL, which means your blood sugar is actually often above 160 mg/dL The American Diabetes Association offers this A1c/ eAG calculator to easily translate your A1c results to an eAG or Average Blood




Insulin Issues Hypoglycemia Diabetes Management




What Is A1c Sugarmds What Is A1c
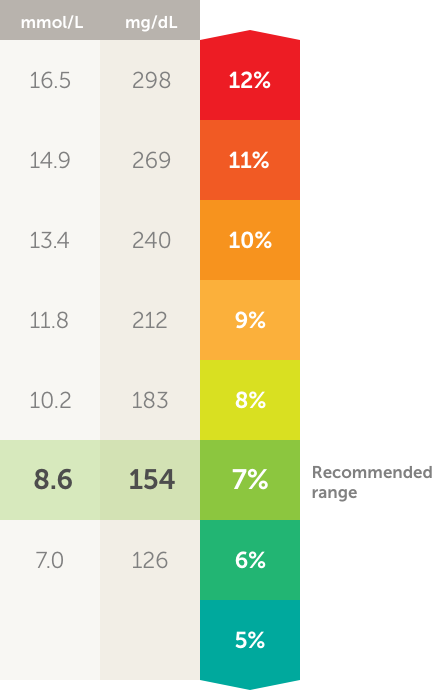
It is defined as the time spent between 70 and 180 mg/dl It simply is a measurement of the ups and downs over a period of time TIR really says it all as it typically gives the percentage of time above 180 and below 70 (see diagram – the yellow section is time spent above 180 mg/dl, the green is between 70 and 180, the red is below 70 andConversion Table for Blood Glucose Monitoring People from outside the US may find this table convenient for converting US blood glucose values which are given in mg/dl into values generated by their blood glucose meters, which are generated in mmol/L mmol/LIt's a way that health professionals can report an A1c result to you in the same measurements you're used to, either mg/dl or mmol/l Take this chart as an example A1c % mg/dL mmol/l 57 117 65 6 126 7 65 140 78 7 154 86 You can use this calculator to work out your estimated average glucose Commonly asked questions



Starting Insulin By M Daoud




Pdf Predictive Value Of Admission Hemoglobin A1c On Inpatient Glycemic Control And Response To Insulin Therapy In Medicine And Surgery Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Semantic Scholar
Mg/dl 40 42 44 46 48 50 52 54 56 58 mmol/L 22 23 24 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 mg/dl 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76 78 mmol/L 33 3We help you interpret your blood sugar values You have tested your blood sugar fasting and the result was 180 mg/dl The corresponding A1C is 79%>180 mg/dl If hypoglycemia occurs or fasting blood sugar is < 80 mg/dl reduce the dose by 4 units or 10 % whichever is greater Goal for FASTING blood sugar 80 130 mg/dl Goal for 2 hour postprandial is



A1c Blood Sugar Calculator Tracker Diabetes App For Android Apk Download




Why Test Glycomark
Diabetes is diagnosed at 2 hour blood sugar of greater than or equal to 0 mg/dl Result Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) Normal less than 140 mg/dl Prediabetes 140 mg/dl to 199 mg/dl Diabetes 0 mg/dl or higherA healthy blood sugar level is between 70 and 130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) before meals and less than 180 mg/dL one to two hours after the start of a meal, according to the American Diabetes Association Three tests are commonly used to measure blood sugar levels A random plasma glucose test is a blood test that is done at any time of day(TIR), with the common default range of 70–180 mg/dL The more TIR the better the A1C is likely to be because these two variables are highly correlated For optimal management, patients should have a TIR level as high as possible with a very low level of time in hypoglycemia




A1c Blood Sugar Calculator Tracker Diabetes App For Android Apk Download




6 Glycemic Targets Standards Of Medical Care In Diabetes 21 Diabetes Care
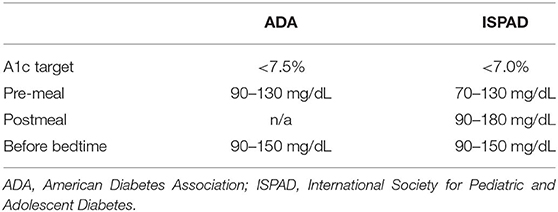
The formula for converting a1c to an estimated average blood glucose level, reports the american diabetes association, is (287 x a1c) – 467 = estimated average glucose thus, the first step for performing the reverse calculation is to add 467 to your average blood glucoseTo convert an a1c to the new average mean blood glucose, use this formula eag(mg/dl) = (287 xA1C to Blood Glucose Conversion Table Use this table to see how an A1C test result correlates to average daily blood sugar Although this is as important as the A1C is, it's not a substitute for frequent self monitoring Only regular blood sugar checks show you howBefore meals 80 to 130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) 1 to 2 hours after meals Lower than 180 mg/dL Youth (younger than 18 years old) with type 1 diabetes A1c Lower than 75% Before meals 90 to 130 mg/dL Bedtime and overnight 90 to 150 mg/dL Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who could become pregnant




Real A1c Test Result Ningxia Red For Healthy Living Facebook
/hyperglycemia-diagnosis-5ae1f370a18d9e003744cd92.png)



How Hyperglycemia Is Diagnosed
A timeinrange of 50% corresponds to an A1C of approximately 8% Time in Range GoalsAdd 467 to the average blood glucose reading from Step 3 If your average reading was 180, your math is 180 467 = 2267 Step 5 Divide your answer from Step 4 by 287 Using the same example as above, your math is 2267 divided by 287 = 7 This means you have an average hemoglobin A1C of 7 percentBlood sugar 180 mg/dl (999mmol/l) fasting is that good or bad?




Practical Considerations In Clinical Management Guideline Recommended Glycemic Targets In Diabetes A1c Fpg Mg Dl Postprandial Glucose Mg Dl Ada 180 Ppt Download




A1c Vs Blood Sugar Measurements Cornerstones4care
Less than 180 mg/dl if you have diabetes Levels in the Morning For example, if your A1c value is 78 (a reading between mg/dl) would be considered high Glycated Hemoglobin (A1C or Hba1c) Value Estimated Average Glucose (EAG) 56% (Highest "normal" value) 114 mg/dlThe HbA1c tool calculates your average blood glucose level in (mg/dl) units The glycated Hemoglobin A1C test shows your average blood sugar level over the past 2 to 3 months If you'd like to know your average blood sugar level over that time frame, just enter your most recent (glycated Hemoglobin test) HbA1c results into the A1c calculator below, then hit enterBlood sugar 180 mg/dl (999mmol/l) is that good or bad?




Blood Sugar Level Chart And Diabetes Information Disabled World



Frontiers Monitoring Of Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes Endocrinology
Regarding the higher number of 231 mg/dL, everybody, nondiabetics included, normally experience a blood sugar spike after a meal Your average postmeal high of 231 mg/dL is equivalent to an A1C of 96% Daily Averages Your daily glucose averages is not going to tell you as much as having your A1C number checked every three months to see whatBackground As the use of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) increases, there is a need to better understand key metrics of time in range mg/dL (TIR ) and hyperglycemia and how they relate to hemoglobin A1c (A1C) Methods Analyses were conducted utilizing datasets from four randomized trials encompassing 545 adults with type 1 diabetes (T1D) who had central The A1C result is significant for longterm glucose monitoring It helps to know how well or bad your past three months of blood glucose control A1C test in % is confusing, because we used to measure glucose levels in mg/dl or mmol/l A1C chart help convert A1C in % to its equivalent average blood glucose, which is easier to interpret




Diabetes Pamphl Elsa Harmon By Elsaharmon Issuu



Glycated Hemoglobin Hba1c Or A1c Calculator
Before a meal 80 to 130 mg/dL Two hours after the start of a meal Less than 180 mg/dL Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors The A1C goal for most adults with diabetes is between 7% and 8%, but your goal may be different depending on your age, other Because A1c is simply a measure of your average blood sugar over 23 months, it can (in theory) decrease by any amount over that time period If you, from one day to the next, decreased your daily average blood sugar from 300 mg/dl (167 mmol/l) to 1 mg/dl (67 mmol/l), your A1c would decrease from 12% to 6% in around two monthsPersonal target ranges for the glucose are typically between 70 to 90 mg/dL (39 to 50 mmol/L) at the low end to 140 to 180 mg/dL (78 to 10 mmol/L) at the high end 1 Glucose and A1c Goals and Targets for Adults () * Diabetes Care ;



How To Lower Your A1c The Complete Guide Diabetes Strong




A1c To Blood Glucose Conversion Table
Additionally, time below target ( The recommended A1c is 57 to 7 An A1c of 12 means your average blood sugar is 298 mg/dl "The American Diabetes Association classifies blood sugar as high when glucose levels are above 180 mg/dl one to two hours after you eat 130 mg/dl before you eat 100 mg/dl when fasting" It is unrealistic to go from a 12 A1c to a 57 overnightHere we have converted eAG 1 mg/dL to A1C Blood Sugar We will also show you what formula we used to convert it Below we have displayed eAG 1 mg/dL converted to A1C percent A1C 58% We converted eAG 1 mg/dL to A1C with this formula (467 eAG) / 287 = A1C and then we rounded the answer to the nearest one decimal Convert eAG 121 mg/dL



A1c Chart Calculator Video Dailymotion




Beyond The A1c Targets For Blood Glucose And Methods Of Measurement Cardi Oh
By contrast, A1C is an indirect measure of blood glucose, since it is dependent on red blood cell turnover (and that varies between people quite a bit;



Starting Insulin By M Daoud



Sa1s3 Patientpop Com Assets Docs 1656 Pdf




Defining Normal A1c Levels Diatribe Org




A1c Calculator Diabetes Blog The Hangry Woman



Ada Jdrf Type 1 Diabetes Sourcebook Excerpt 13 Setting Treatment Targets Part 2 Of 2




Going Beyond A1c One Outcome Can T Do It All Diatribe



A1c To Mg Dl Conversion Chart




6 Glycemic Targets Diabetes Care




A1c Levels And What They Mean Diabetic Live



Normal Blood Sugar Levels For Diabetics And Non Diabetics



Why Are We Waiting To Treat Diabetes Until A1c Reaches 6 5




6 Glycemic Targets Standards Of Medical Care In Diabetes Diabetes Care




Pin On Diabetes




12 A1c Charts And Ideas Diabeties Diabetes Information Diabetic Diet



The Power Of The Cgm




What Do Your A1c Test Results Really Mean
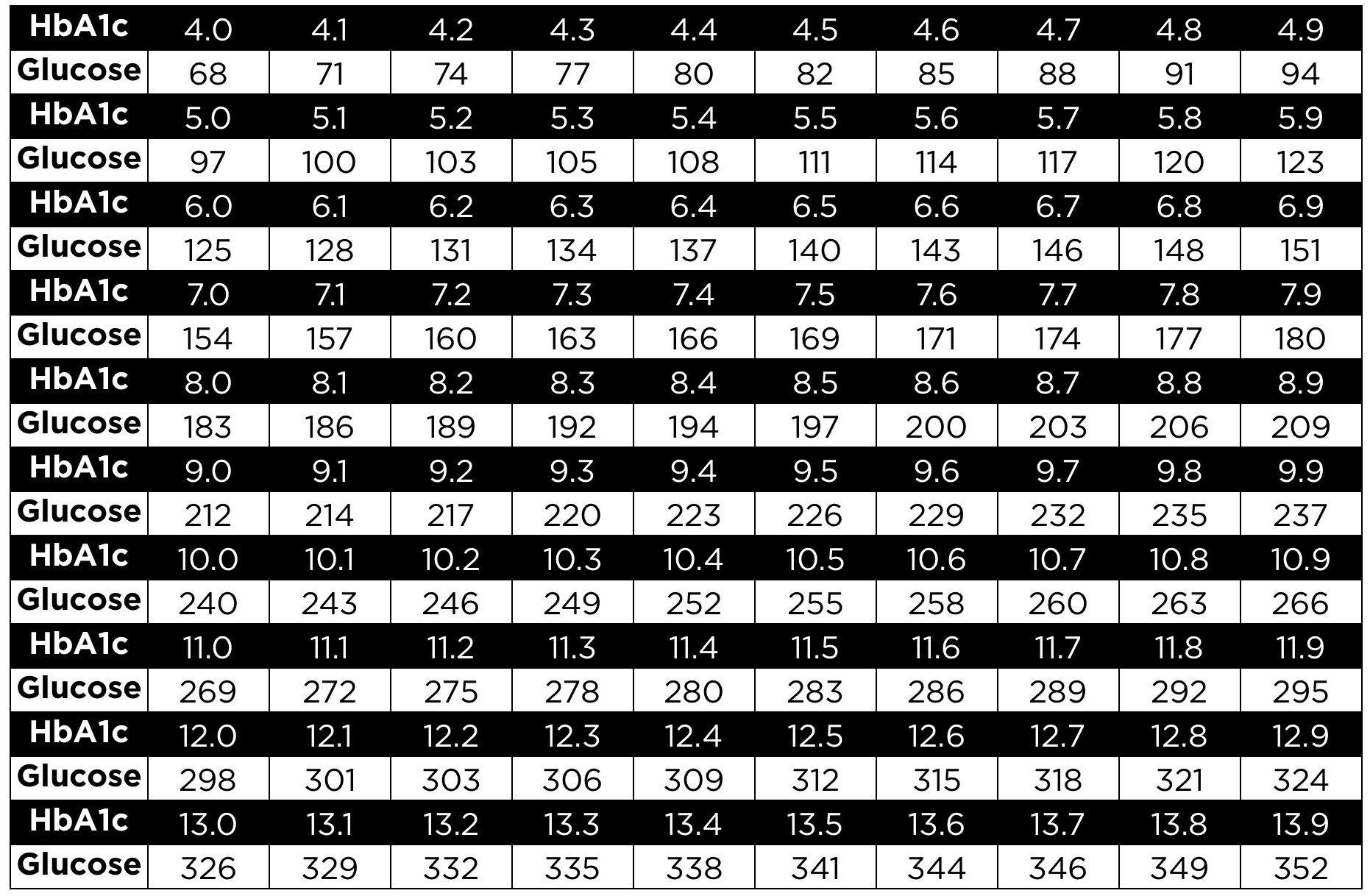



A1c Calculator For Average Blood Sugar Level Diabetes Knowledge



Pdf Reference Intervals For Hemoglobin A1c Hba1c In Healthy Mexican Pregnant Women A Cross Sectional Study



How To Lower Your A1c The Complete Guide Diabetes Strong




Is Your Blood Sugar High And What To Do About It




The Future Of Pumping Henry Anhalt Do Cde Ppt Video Online Download




Associations Between A1c And Continuous Glucose Monitoring Derived Glycemic Parameters Diabetes




6 Glycemic Targets Diabetes Care



1




Time In Range Diatribe



How To Know If Your Blood Sugar Levels Are Healthy Business Insider




A1c Blood Sugar Calculator Tracker Diabetes App For Android Apk Download




A1c Blood Sugar Calculator Tracker Diabetes App For Android Apk Download




A1c Conversion Chart Diabetestalk Net



A 1 C C H A R T P R I N T A B L E Zonealarm Results




Approach To The Perioperative Management Of Diabetes Hba1c Hemoglobin Download Scientific Diagram




Discussion Hemoglobin A1c Levels




Using The Gmi To Estimate Your A1c How Accurate Is It Diatribe




Time In Range Hormone Health Network



How Do Blood Sugar Levels Correlate To A1c Quora




Defining Normal A1c Levels Diatribe Org




Prevalence Total 8 Million Children And Adults Of The Population Have Diabetes Diagnosed 14 6 Million People Undiagnosed 6 2 Million Ppt Download
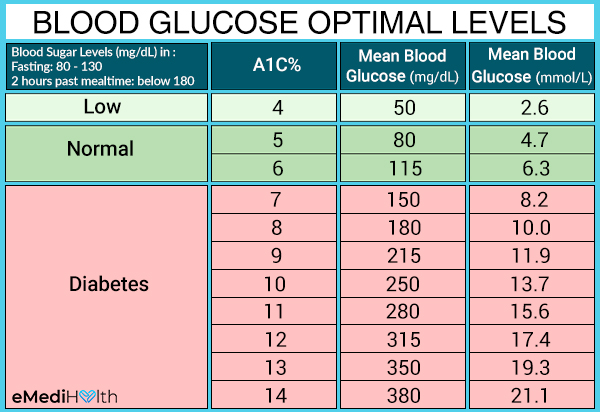



Diabetes 101 How To Lower Blood Sugar Levels Emedihealth
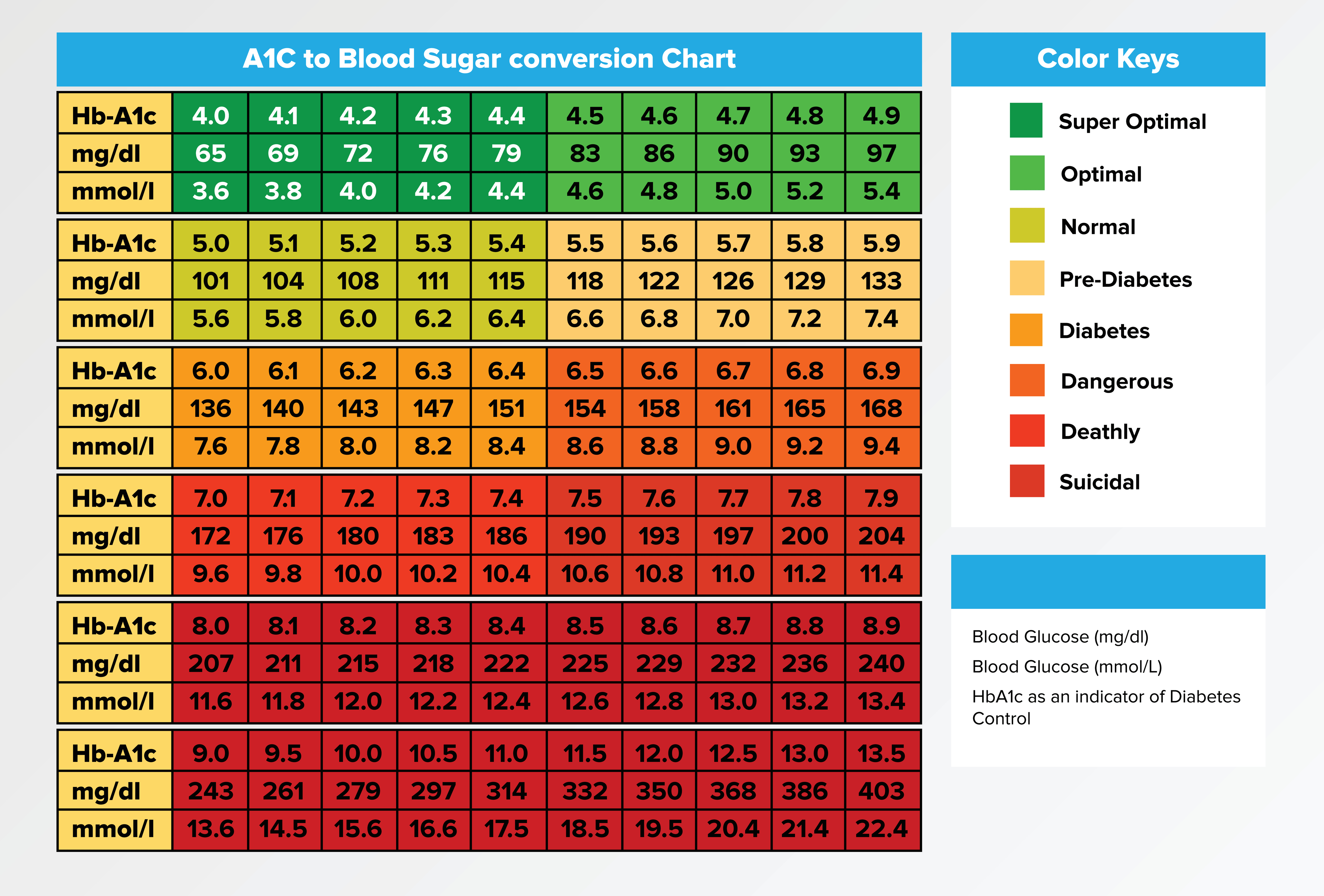



Hba1c Hemoglobin A1c A1c Chart Test Levels Normal Range




Best A1c Chart And All Hgb A1c Levels Charts Blood Test Results Explained




Pdf Determinants Of Hemoglobin A1c Level In Patients With Type 2 Diabetes After In Hospital Diabetes Education A Study Based On Continuous Glucose Monitoring



What Is The Normal Glucose Level For A Teenager Quora




Management Of Diabetes Treat To Target Approach A1c 7 By Professor Dr Intekhab Alam Department Of Medicine Postgraduate Medical Institute Lady Reading Ppt Download




A1c Conversion Chart Diabetestalk Net




Pin On Reversing Type 2 Diabetes
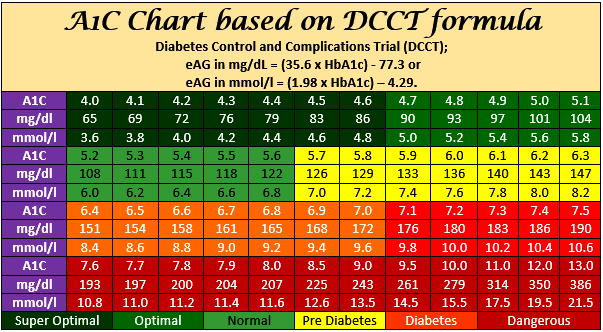



A1c Chart A1c Level Conversion Chart Printable Pdf
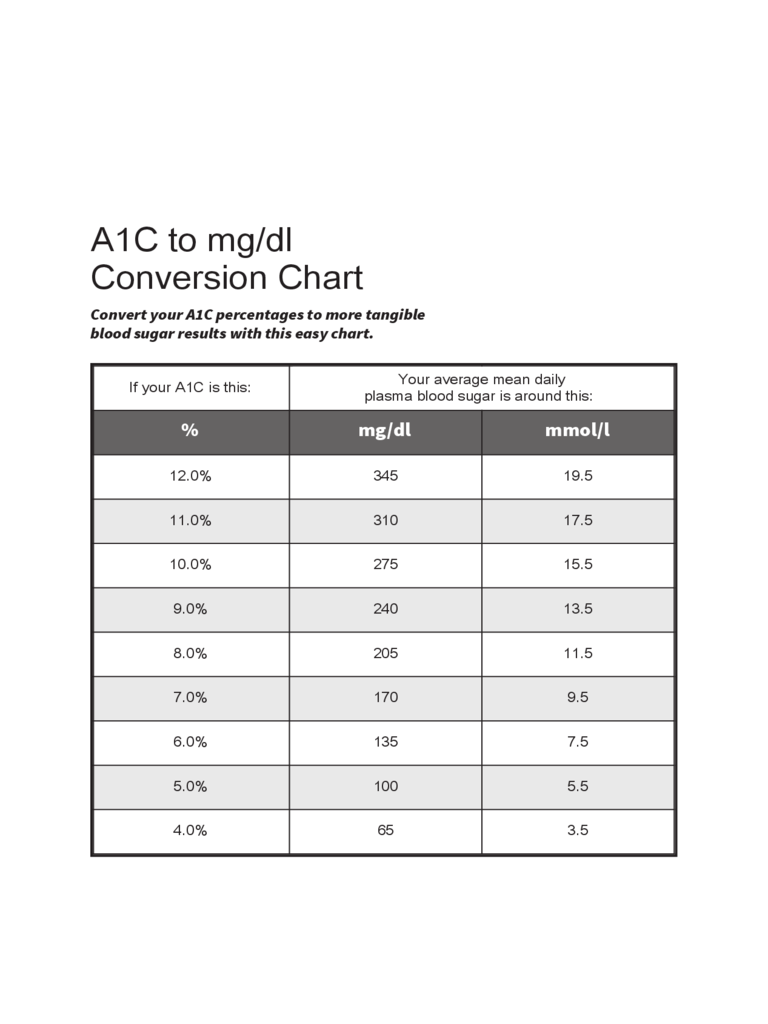



A1c To Mg Dl Conversion Chart Edit Fill Sign Online Handypdf



Fructosamine To A1c Converter Not Dead Diabetic



Clinical Case 54 Year Old Lawyer Diabetes Diabetes Rounds



Rule Of Thomas For Hemoglobin A1c Conversion Diabetic Solutions Videosdiabetic Solutions Videos




Optimal Plasma Glucose And A1c Goals For Youths With Type 1 Diabetes Download Table




Prodigy Diabetes Care Benefits Of Testing



Hb A1c To Average Blood Glucose Conversion Table In Mg Dl And Mmol L
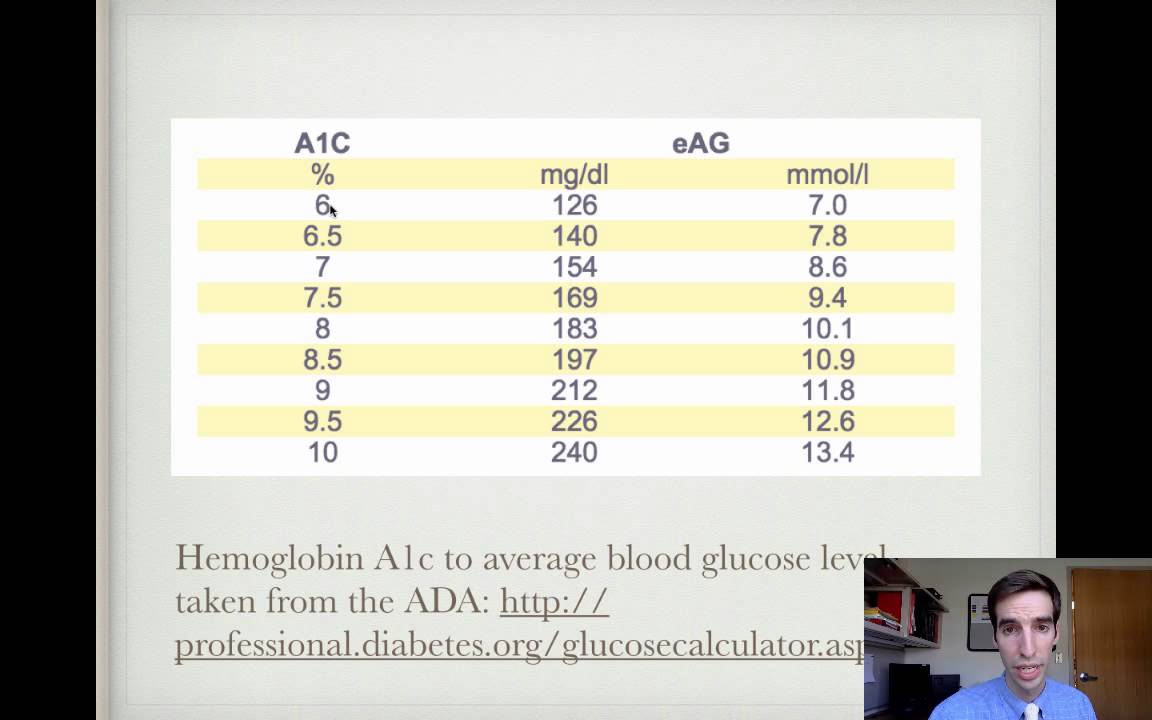



Rule Of Thomas For Hemoglobin A1c Conversion Youtube




Translating Your A1c To A Blood Sugar Level Type 2 Nation




Diatribe Twitter પર To Determine Timeinrange Tir Use 14 Day S Worth Of Blood Glucose Data For Those With T1d Or T2d Aim For 70 Of The Day In 70 180 Mg Dl Blood



Q Tbn And9gcqkwysnrnewjze T46kj1gbg7kr2l0njzfhpbi39z7nfhhg1cf4 Usqp Cau




Diabetes Medications Update Ppt Download
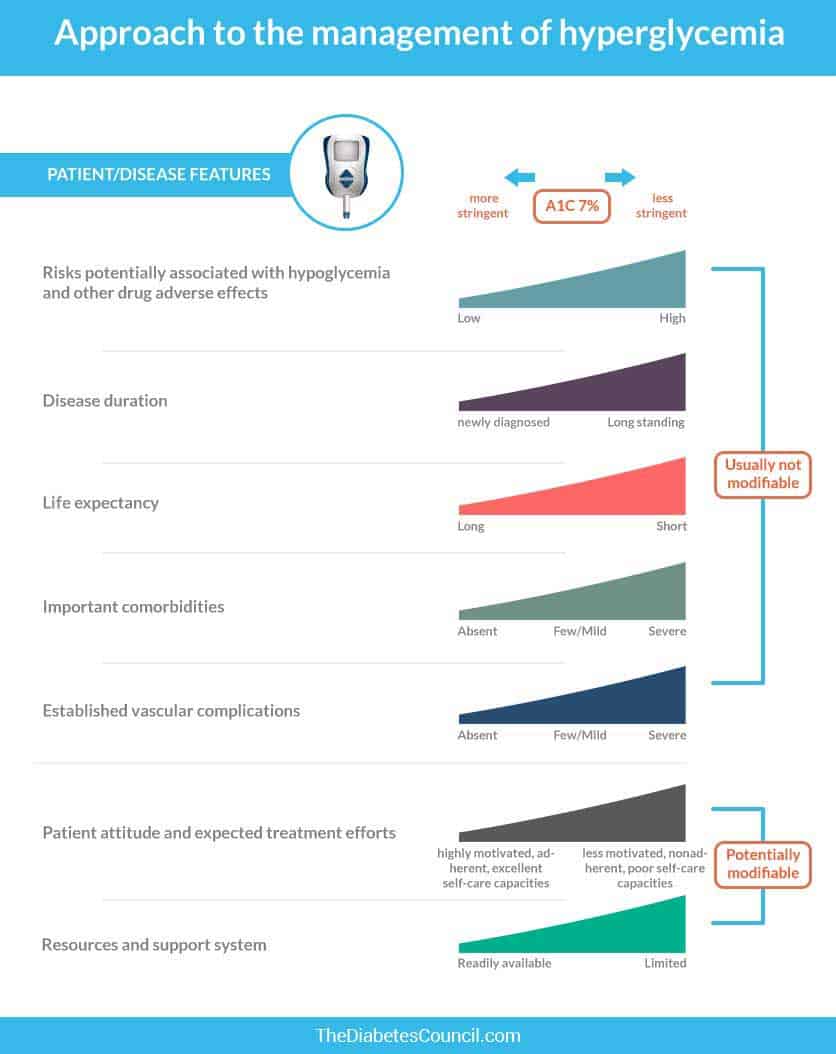



What Are Blood Sugar Target Ranges What Is Normal Blood Sugar Level Thediabetescouncil Com




Hemoglobin A1c Test Hba1c Normal High Low Levels Charts Results




Why The A1c Sucks And Why Time In Range Is More Important Taking Control Of Your Diabetes




Basal Bolus Regimen In T2dm Ppt Download



Search Q Type 2 A1c Chart Tbm Isch
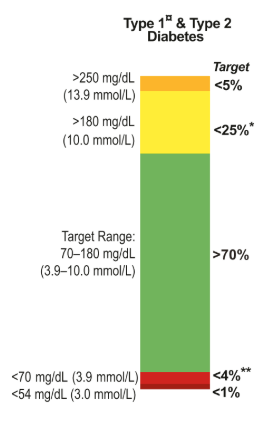



A1c Vs Time In Range What Is A1c What Is Time In Range How By Niloufar Novin Steady Health
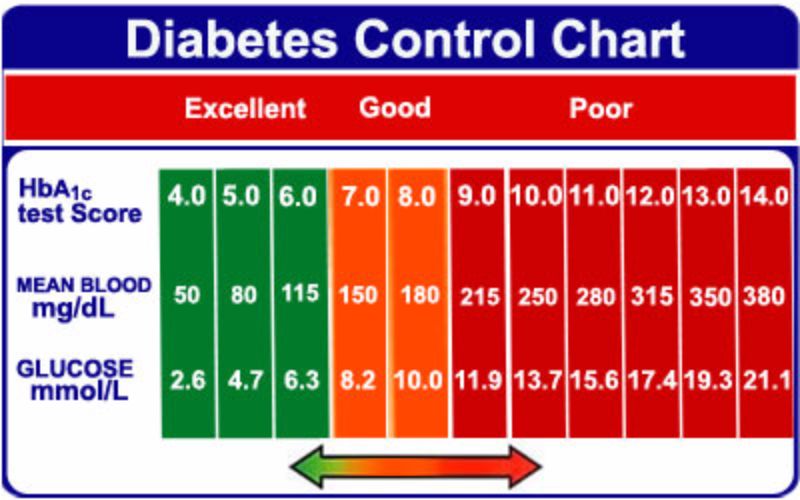



25 Printable Blood Sugar Charts Normal High Low ᐅ Templatelab




Glucose Management Indicator Gmi A New Term For Estimating A1c From Continuous Glucose Monitoring Diabetes Care



How To Calculate Your A1c Glucosetracker Net




Prediabetes Tests A1c Test 3 Glucose Tests And More




Blood Sugar To A1c Conversion Chart Diabetestalk Net




Understanding Your Hba1c Diabetes Self Management
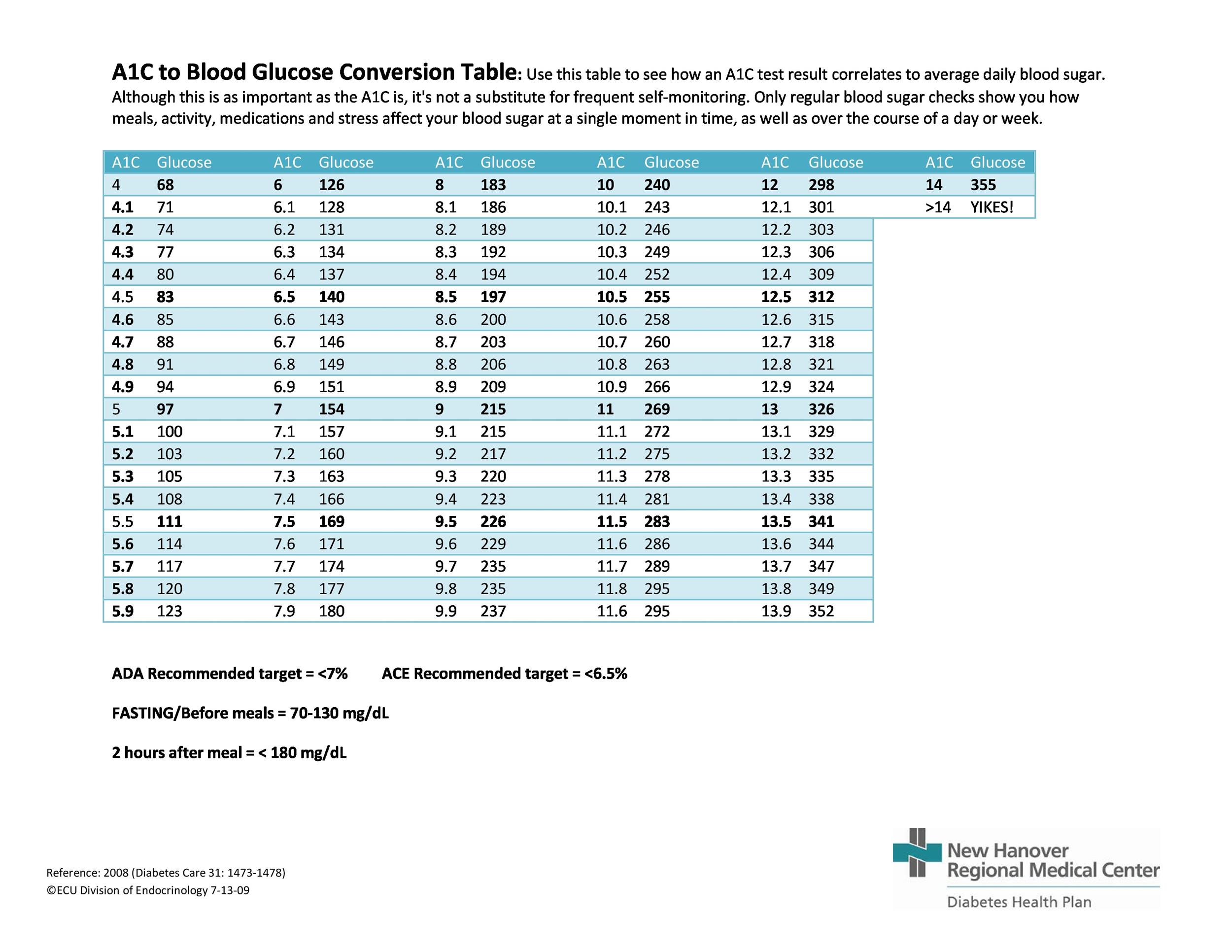



25 Printable Blood Sugar Charts Normal High Low ᐅ Templatelab



Q Tbn And9gctokau840 Eozzmtfajmye7lduvuwt418vxo4dwzau Usqp Cau
.jpg)



Time In Range Diatribe




Rd Is Tir A Scam A1c Is An Excellent Metric Tir Has 180 Mg Dl As An Upper Bound More Than Double Normal Why Is Tir Then Desirable Because Your Protocol



What Is A1c Test For Diabetic A1c Test Definition




Getting To Normal Usaasc




What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level Diabetes Self Management




A1c Tip Change Your Goal Blood Sugar Range Natalyah Coaching



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿